Transformer
This post covers Transformer architecture. Heavily referenced to Josh Starmer’s StatQuest Transformer Neural Networks, ChatGPT’s foundation, Clearly Explained!!! video.
Table of contents
Positional Encoding
Although “Nik eats ravioli” and “Ravioli eats Nik” use exact same vocabulary, two sentences mean totally different thing. As you know, words’ order is very important task. To do this jon, we use Positional Encoding. About this topic, content here explains amazingly.
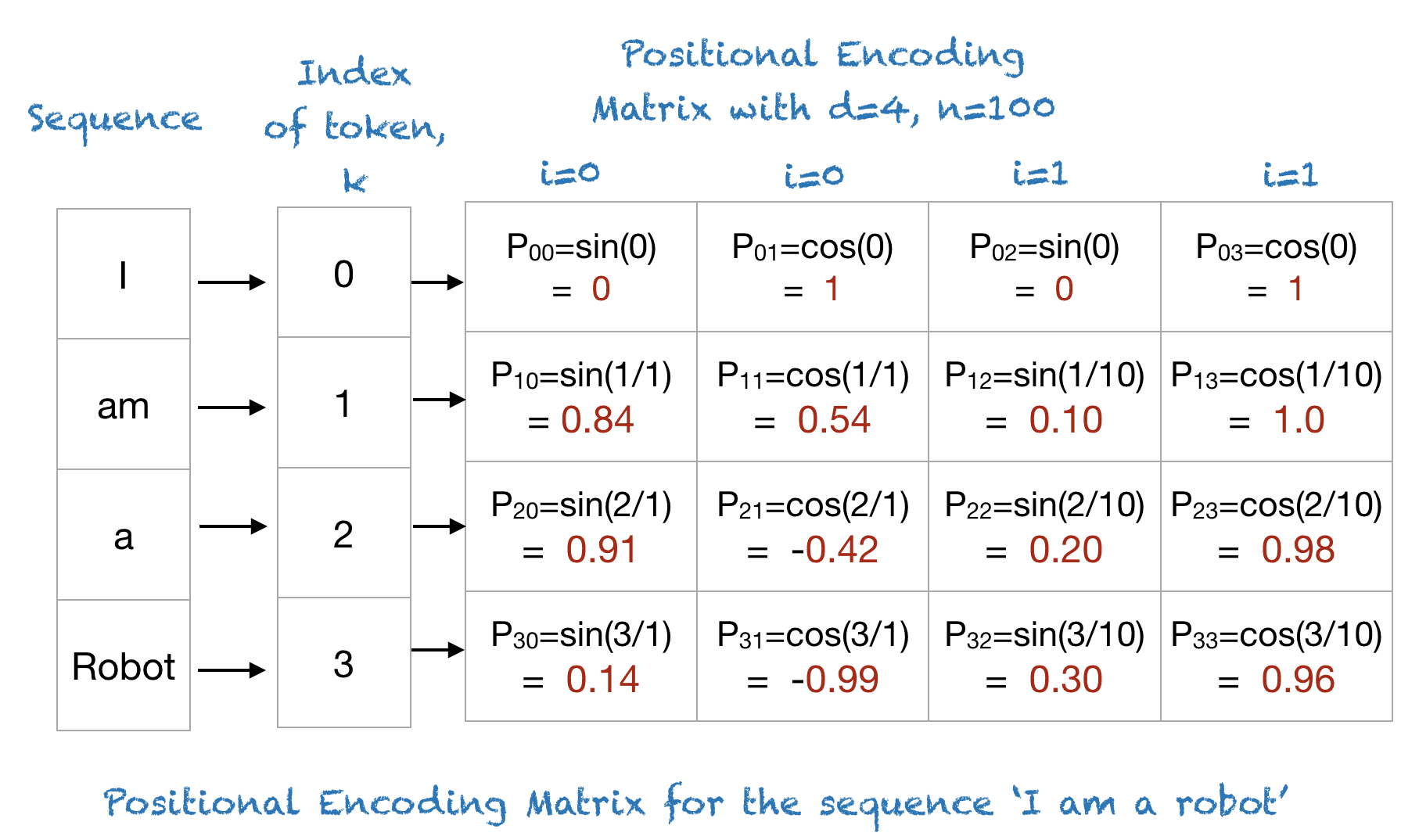 Positional Encoding Diagram1
Positional Encoding Diagram1
- Coverts words “Nik eats ravioli” into numbers using Word Embedding.
- Add a set of numbers that correspond to word order to the embedding values for each word.
-
Where the set of number come from? The numbers that represent the word order come from a sequence of alternating Sine and Cosine squiggles.
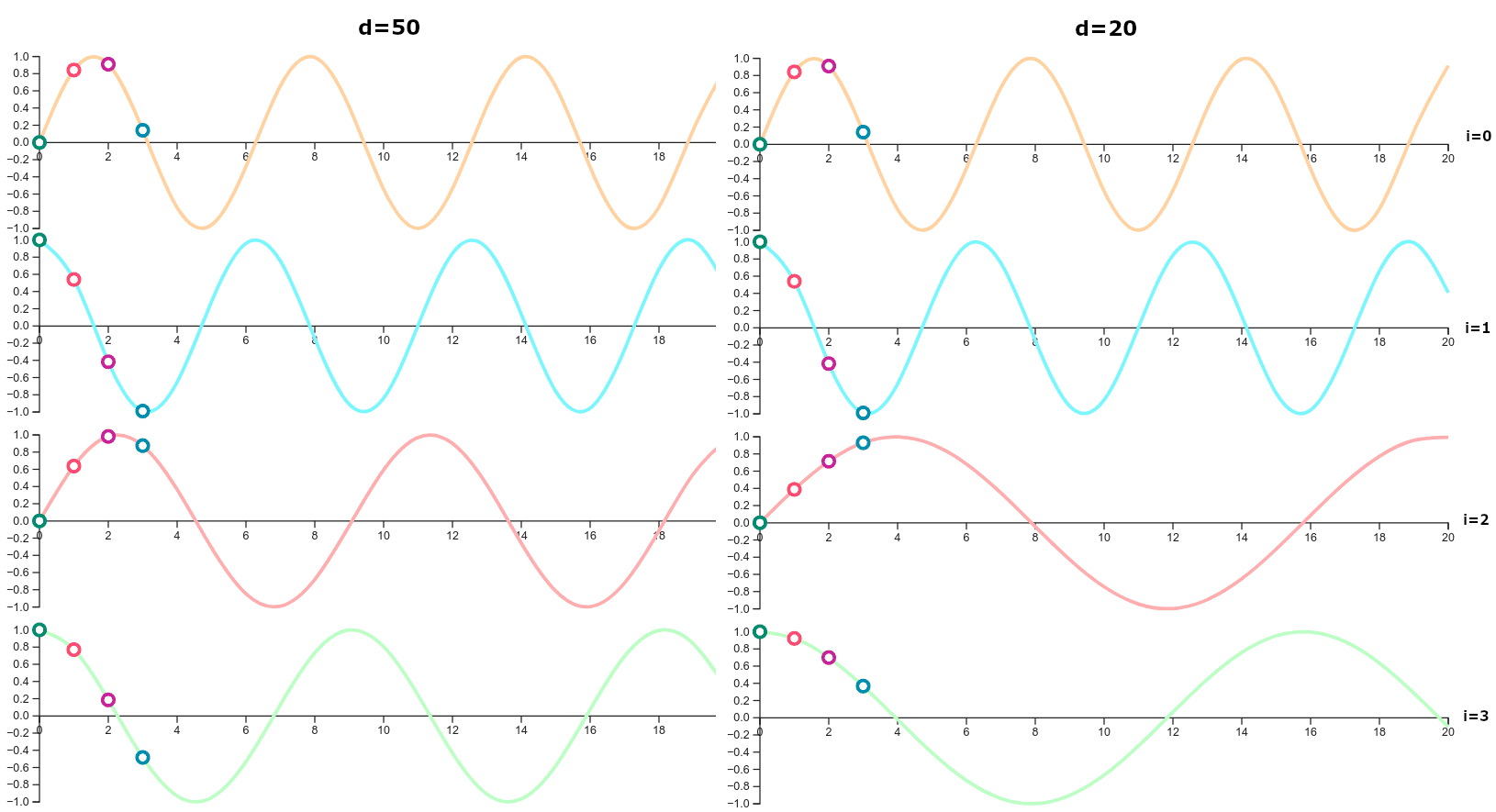 Usage of Sine and Cosine Token for Positional Encoding2
Usage of Sine and Cosine Token for Positional Encoding2But why repetitive Sine and Cosine graphs? Isn’t it possible to have two different words might get the same position, or values?
Yes, that’s right. But since we have different width of Sine/ Cosine embedding squiggles through out different positions and multiple positional encoding cells per word, even with a repear value here and there, we end up with a unique sequence of position values for each word.
-
Finally, we add Word Embedding values and Positional Encoding values.
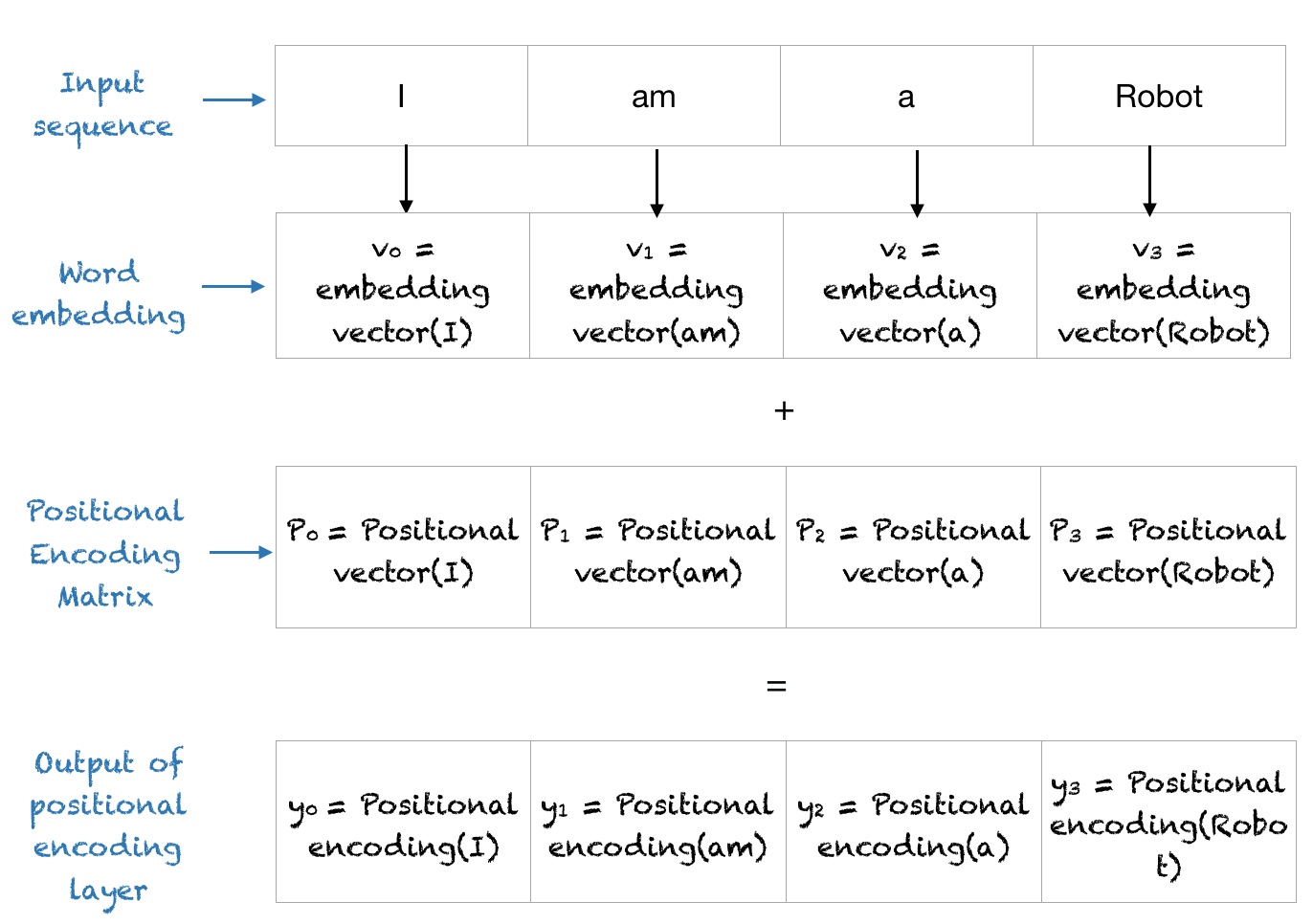 Positional Encoding Process3
Positional Encoding Process3- If we change the order of a sentence, then the order of word embedding values changes, but the order of positional encoding values remains. Therefore, by adding up two values we get new positional encodings.
Self Attention
Main Idea
This concept tells how Transformer keeps track of the relationships among words. In general terms, Self-Attention works by seeing how similar each word is to all of the words in the sentence, including itself. To be specific, Self-Attention calculates these similarities for every word in the sentence. Once the similarities are calculated, they are used to determine how the Transformer encodes each word. After numerous training, transformer will eventually learn which word more relates to other words.
Process
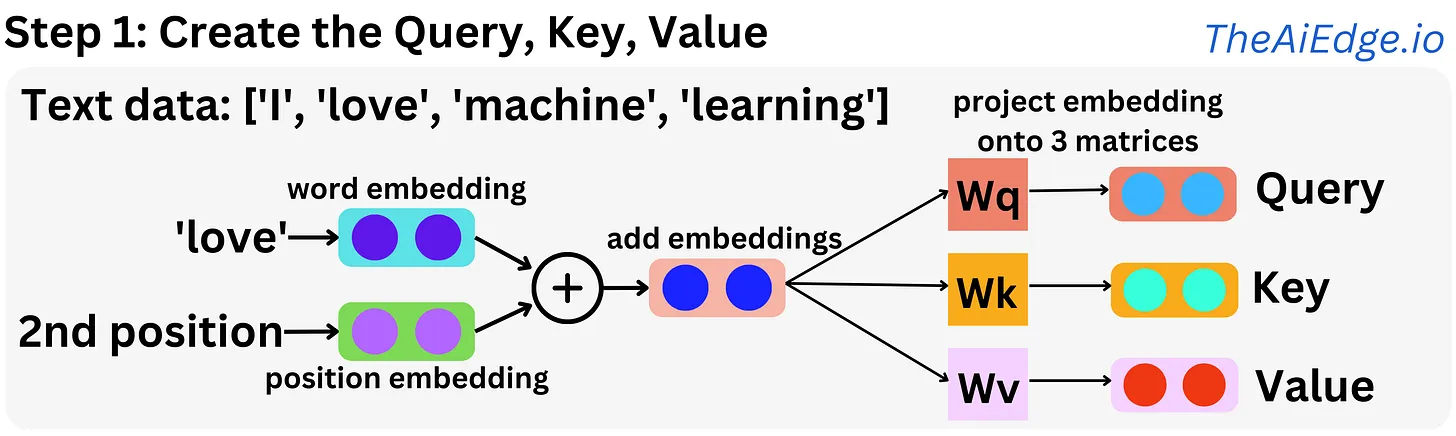 Query, Key, Values4
Query, Key, Values4
- Get Query Values for each word.
-
Multiply Positional Encoding(word embedding + positional vlaue) with another weights and get query values.
Why do we need query values instead of using word embedding values directly?5
If we think of Self-Attention as a unit with it’s weigths for calculating Queries, Keys, and Values, as a Self-Attention Cell, in order to correctly establish how words are related in complicated sentences and paragraphs we can create a stack of self-attention cells, each with it’s own sets of weights that we apply to the Position Encoded values for each word, to capture different relationships among the words.
In the manuscript that first described transformers, they stacked 8 Self-Attention Cells, whichi is also called Multi-Head Attention.
-
- Generate Key Values similar to how we get query values.
- So, let’s say we have query values and key values for word A and key values for word B. We use key values to calculate similarities to the query’s for word A.
- One way to calculate similarities between the query and keys is to calculate Dot Product.
- As a result, dot product of word A query with its key will produce relatively large similarity value to the result of word A query with word B’s key value.
- Since word A is more similar to itself than it is to the word B, we want to have more influence on its encoding that the word B.
- To do this, we first run the similarity scores through SoftMax function.
- For example, since we input the similarity result of the word A itself and word B, we could imagine that the output of SoftMax of these values end up in 1.0 and 0.0.
-
After calculating SoftMax, we make another set of values, that are called Value. Then scale the Values that represent the word A by 1.0(SoftMax output of word A to A). We do the exact same process for word B, except we scale Values byt 0.0(SoftMax output of word A to B). And finally, we add these scaeld values together. → These sums, which combine separate encodings for different words, relative to their similarity to target word, are the Self-Attention values for the target word.
The main idea of SoftMax function is that it preserves the order of the input values, from low to high, and translates them into numbers between 0 and 1 that add up to 1. So we can think of the output of the SoftMax function as a way to determine what percentage of each input word we should use.6
- Next is to calculate Self Attention values for other words. Good news is that we don’t need to calculate Key and Values. All we need to do is to create the Query that represents the word.
 Overall process of calculating Self Attention values7
Overall process of calculating Self Attention values7
- Create Residual Connections We take the Position Encoded values and add them to Self Attention values. These are called Residual Connections and they make it easier to train complex neural networks by allowing the Self-Attention layer to establish relationships among the input words without having to preserve the Word Embedding or Position Encoding information.
Details
- We reuse same sets of Weights for calculating Queries, Keys, and Values for each input words. This means that no matter how many words are input into the Transformer, we just reuse the same same sets of weights.
- We can calculate the Queries, Keys and Values for each word at the same time. → Take advantage of parallel computing and run fast.
Building Decoder
 Encoder-Decoder Architecture8
Encoder-Decoder Architecture8
- Starts with Word Embedding but with the target language.
- Start with
to initiate the decoding process. - Add Positional Encoding using same Sine and Cosine graphs that we used for encoding.
- Add Self Attention layer and calculate self attention values.
- Note: The sets of weights used to calculate the Decoder’s Self-Attention Query, Key and Value are different from the sets that are used in the Encoder.
- Since it’s really important for the decoder to keep track of the significant words in the input, the main idea of Encoder-Decoder Attention is to allow the decoder to keep track of the significant words in the input.
- Create new values to represent the Query for the
token in the decoder. - Then create Keys for each word in the encoder.
- Calculate the similarities between the
token in the decoder and each word in the encoder by calculating dot products. - Run similarities into the SoftMax function to get percentages. → Decoder determines what should be the first translated word.
- Calculate Values for each input words then scale values by the SoftMax percentages.
- Add scaled values to get Encoder-Decoder Attention values.
- Note: We can stack Encoder-Decoder Attention just as we stacked Encoder Attention layers.
- Create new values to represent the Query for the
- Residual Connections.
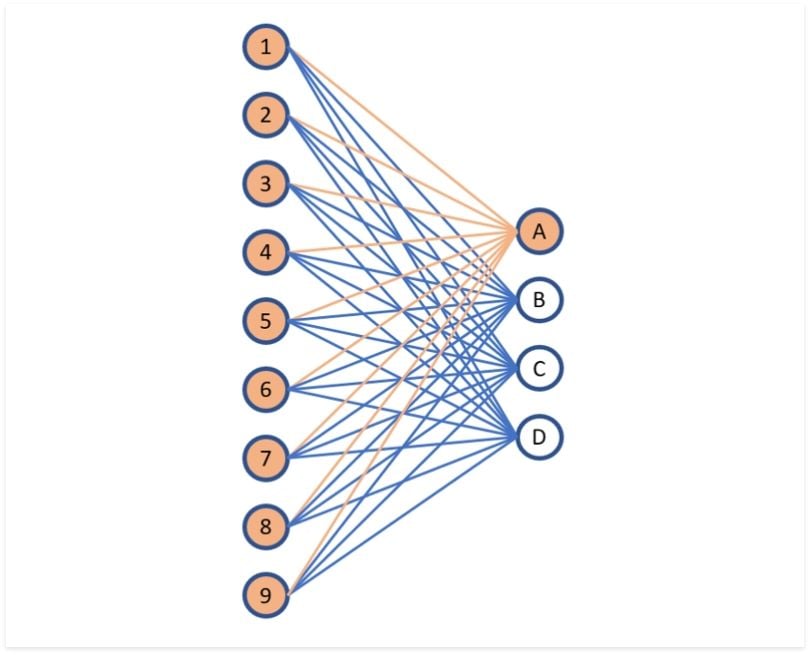 Fully Connected Layer diagram9
Fully Connected Layer diagram9
- We need a way to take Residual Connections values and select one of the output word vectors. To do this, we run these values through a Fully Connected Layer that has one input node for each value that represents current token and one output node for each token in the output vocabulary.
- Finally, run outputs into the SoftMax function to select the first output word.
- Output word becomes input word to feed into the first Word Embedding layer until the algorithm hits
.
Add Ons
- Normalization after every step.
- Different similarity functions other than dot product.
- Additional neural networks with hidden layers to both encoder and decoder to give a transformer more weights and biases to fit to complicated data.
-
Figure from this article, Machine Learning Library ↩
-
Figure from this article ↩
-
Figure from this article, Machine Learning Library ↩
-
Figure from this article, Damien Benveniste, The AiEdge+: Everything you need to know about the Attention Mechanism!, The AiEdge Newsletter ↩
-
Description from this video, StatQuest with Josh Starmer, Transformer Neural Networks, ChatGPT’s foundation, Clearly Explained!!!, 21:37 ~ ↩
-
Description from this video, StatQuest with Josh Starmer, Transformer Neural Networks, ChatGPT’s foundation, Clearly Explained!!!, 18:00 ~ ↩
-
Figure from this paper, Wang, Jian & Li, Mengying & Diao, Qishuai & Lin, Hongfei & Yang, Zhihao & Yijia, Zhang. (2020). Biomedical document triage using a hierarchical attention-based capsule network. BMC bioinformatics. 21. 380. 10.1186/s12859-020-03673-5. ↩
-
Figure from this article, Sudipto Baul, Transformer: The Self-Attention Mechanism, Medium ↩
-
Figure from this article, Diego Unzueta, Fully Connected Layer vs. Convolutional Layer: Explained, builtin ↩